RCIS (CCI) Eligibility for Cath-Lab Nurses & Techs: Pathway Selection, Procedure :
Cardiovascular Credentialing International (CCI) offers certifications and credentials recognizing individuals who focus on the heart and vascular systems.
Apply for New Certifications:
- Apply for Advanced Cardiac Sonographer
2. Apply for Certified Cardiographic Technician
3. Apply for Certified Rhythm Analysis Technician
4. Apply for Registered Congenital Cardiac Sonographer
5. Apply for Registered Cardiac Electrophysiology Specialist
6. Apply for Registered Cardiac Sonographer
7. Apply for Registered Phlebology Sonographer
8. Apply for Registered Vascular Specialist

Which pathway? (simple decision rule)
- Most India-trained cath-lab professionals (e.g., BSc Nursing/Allied Health + cath-lab work) → RCIS235
Why: CCI accepts a health-science diploma/degree + ≥1 year full-time invasive CV (cath-lab) experience + ≥600 cardiac diagnostic/interventional procedures (procedures can be from work and/or during a formal program). - Graduates of a dedicated invasive cardiovascular technology program in India (not US/Canadian programmatically accredited) with ≥1 year specialty training and ≥800 clinical hours → RCIS5. (Those hours must be part of the program; hours done after graduation don’t count toward the 800.)
- RCIS4 applies only if you finished a programmatically accredited invasive CV technology program recognized by CHEA/USDOE/Canadian Medical Association—this is typically US/Canada, so it almost never fits Indian schools.
Bottom line: If you’re a nurse/allied-health graduate from India with ≥1 year cath-lab experience and you can document ≥600 procedures, apply under RCIS235 (this is effectively the “old RCIS-3” bucket). If you completed a formal invasive CV tech program with the built-in 800 clinical hours, use RCIS5.
Documents you’ll need (match to your pathway)
- For RCIS235 (health-science degree + experience + 600 procedures):
- Completion certificate and/or transcript
- Employment Verification Letter (must confirm full-time invasive CV work and number of procedures)
- Clinical Experience Letter only if you’re counting procedures done during a formal education program.
- For RCIS5 (non-programmatically accredited invasive CV tech program with 800 clinical hours):
- Completion certificate and/or transcript
- Student Verification Letter
- Clinical Verification Letter (to confirm the ≥800 clinical hours in the specialty as part of the program).
CCI provides sample Employment, Student, and Clinical verification letters—use these so your hospital/program includes every required line (letterhead, dates, role, hours/procedures, signatory, etc.).

EXAM DETAILS:
FEE -365 USD
Exam conducted by -Pearson Professional centres
CBT Exam
3 hour exam and 170 MCQ
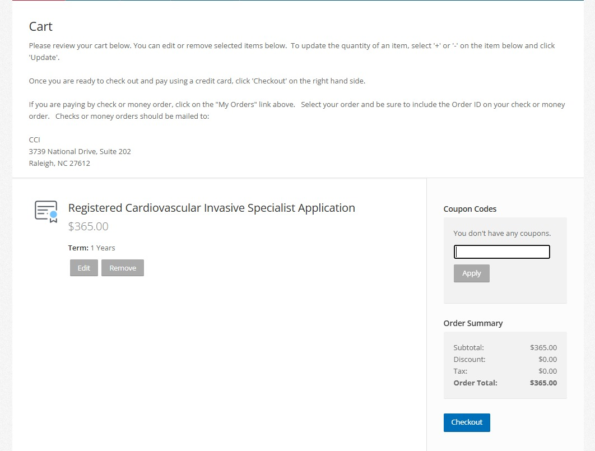
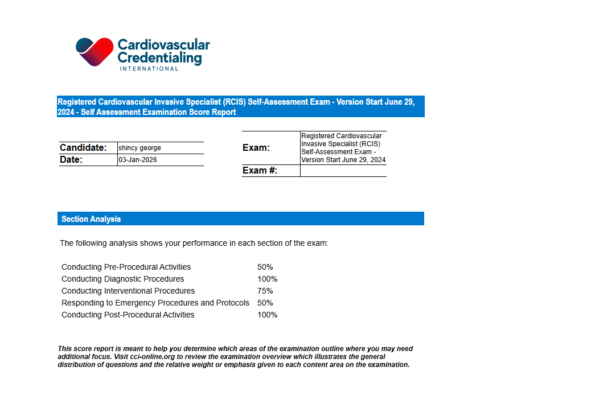
We have specialized study materials for this exam.

If you need assistance for exam booking, study materials and further process, Kindly contact Nursingmanthra WhatsApp number-+971502515717

MODEL QUESTION PAPER :
- What is an advantage to using a filter versus a balloon occlusion distal protection device?
Options:
A. Allows distal perfusion
B. Lower profile of the device
C. Ensures distal vessel occlusion
D. Allows small embolic particles to pass
✅ Correct Answer: A. Allows distal perfusion
Rationale (Short):
A filter-based distal protection device captures embolic debris while still allowing blood flow (distal perfusion). In contrast, balloon occlusion devices temporarily stop distal flow during the intervention and require aspiration before restoring perfusion.
2. Question: What type of valvuloplasty requires a transseptal puncture?
Options:
A. Aortic
B. Mitral
C. Tricuspid
D. Pulmonary
✅ Correct Answer: B. Mitral
Rationale (Short):
Percutaneous mitral balloon valvuloplasty (e.g., Inoue balloon for mitral stenosis) is typically performed via a venous approach and requires transseptal puncture to access the left atrium and then cross the mitral valve. Aortic and pulmonic valvuloplasty are usually approached directly (arterial for aortic, venous for pulmonic) without transseptal access.
3. Question: What is the MOST COMMON complaint of a patient with mitral valve regurgitation?
Options:
A. Angina
B. Insomnia
C. Claudication
D. Shortness of breath
✅ Correct Answer: D. Shortness of breath
Rationale (Short):
Mitral regurgitation increases left atrial pressure and pulmonary venous congestion, leading most commonly to dyspnea (shortness of breath)—especially on exertion (and later orthopnea/PND).
4. Question: What is the primary mechanism behind the coronary no-reflow phenomenon?
Options:
A. Spasm of the coronary artery
B. Dissection of the coronary artery
C. Mechanical obstruction by a stent
D. Microvascular dysfunction and distal embolization
✅ Correct Answer: D. Microvascular dysfunction and distal embolization
Rationale (Short):
No-reflow occurs when the epicardial artery is open but tissue perfusion remains poor due to microvascular obstruction (distal embolization of plaque/thrombus debris, endothelial swelling, inflammation, and microvascular spasm). Spasm/dissection/stent obstruction typically cause epicardial flow limitation, not classic no-reflow.
5. Question: What is the first-line treatment for a coronary perforation identified during PCI?
Options:
A. Use of a covered stent
B. Administration of thrombolytics
C. Immediate coronary artery bypass graft
D. Prolonged balloon inflation at the site of the perforation
✅ Correct Answer: D. Prolonged balloon inflation at the site of the perforation
Rationale (Short):
The immediate first step is to control bleeding by tamponading the perforation with prolonged balloon inflation at/near the site. A covered stent or embolization may be needed if bleeding persists, and surgery is reserved for uncontrolled cases. Thrombolytics are contraindicated because they worsen bleeding.
6. Question: During an echocardiography-guided transseptal procedure, _____ describes what is observed when the transseptal catheter makes contact with the _____.
Options:
A. Tenting; fossa ovalus
B. Tapping; fossa ovalus
C. Tenting; crista terminalis
D. Tapping; crista terminalis
✅ Correct Answer: A. Tenting; fossa ovalus
Rationale (Short):
When the transseptal sheath/needle presses on the fossa ovalis, echocardiography shows a characteristic “tenting” (bowing) of the interatrial septum—confirming appropriate positioning before puncture. The crista terminalis is a right atrial ridge and is not the intended puncture site.
7. Question: What complications are MOST FREQUENTLY associated with vascular closure devices? Choose THREE responses.
Options:
A. Infection
B. Thrombosis
C. Device failure
D. Delayed bleeding
E. Acute hemorrhage
✅ Correct Answers: A. Infection, C. Device failure, D. Delayed bleeding
Rationale (Short):
The most common closure-device–related problems are device failure/maldeployment and access-site bleeding/oozing (often delayed). Because a closure device introduces foreign material and a puncture tract, local infection is also a recognized frequent complication. Thrombosis/arterial occlusion and major acute hemorrhage can occur but are less common compared with failure/bleeding-type issues.
8. Question: When performing FFR, what is the threshold that indicates a significant stenosis?
Options:
A. 0.7
B. 0.8
C. 0.9
D. 1.0
✅ Correct Answer: B. 0.8
Rationale (Short):
Fractional Flow Reserve (FFR) is the ratio of distal coronary pressure to aortic pressure during maximal hyperemia. An FFR ≤ 0.80 is generally considered hemodynamically significant (ischemia-producing) and may benefit from revascularization, depending on clinical context.
9. Question: When advancing a Swan-Ganz (PA) catheter in a patient with left bundle branch block (LBBB), what emergency intervention may be required?
Options:
A. Fluid bolus
B. Temporary pacing
C. Intra-aortic balloon pumping
D. Synchronized cardioversion
✅ Correct Answer: B. Temporary pacing
Rationale (Short):
Advancing a PA catheter can irritate the right bundle and cause a transient right bundle branch block (RBBB). In a patient who already has LBBB, developing RBBB can result in complete heart block, so temporary pacing may be needed immediately.
10. Question: In preparation for a pericardiocentesis, the patient should be at a ____ degree angle.
Options:
A. 0–15
B. 30–45
C. 55–70
D. 75–90
✅ Correct Answer: B. 30–45
Rationale (Short):
Pericardiocentesis is commonly performed with the patient in a semi-Fowler position (about 30–45°). This helps pool the pericardial fluid inferiorly/anteriorly, improves access (often subxiphoid or apical approach), and can enhance imaging guidance.
















